We have spent plenty of time outlining why San Diego’s Tap Water Is So Bad, but what is the process that the city uses to attempt to clean it?
Overall, the city does the best it can to disinfect the water we import from the Colorado River and Northern California, but it doesn’t remove everything harmful; San Diego has a relatively high total dissolved solids (TDS) count in its water.
Water treatment isn’t all about removing substances though – the city also adds chlorine, ammonia, sodium hydroxide and fluoride before sending it to your home.
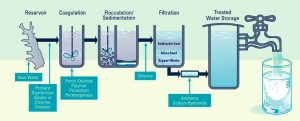
The Disinfection Process
#1. Primary Disinfection with Ozone or Chlorine Dioxide to inactivate viruses, bacteria and other pathogenic organisms. While this process is pretty effective in killing off nasty stuff, there are still chlorine-resistant parasites such as cryptosporidium and giardia in our water.
#2. A chemical mixture is added to remove dissolved solids.
#3. Chlorine is added again for further disinfection.
#4. Water is filtered over a coal and sand composite to remove small particles.
#5. Ammonia is added (creating dangerous chloramines) to prevent microbial growth, and sodium hydroxide is added to correct the pH of the water.
#6. As mandated by California state law, Fluoride is added to the water to ‘promote strong teeth’. And as we outlined, HERE, this is an issue.
Next, the water is sent to your tap.
The California Department of Public Health (CDPH) has a list of some contaminants it requires the City of San Diego to monitor. There are still hundreds of thousands of harmful contaminants that do not require monitoring.
The 2013 Annual Drinking Water Quality Report states that during 2013, contaminants requiring monitoring were detected at or above Detection Limits for Purposes of Reporting. They issued this warning:
“Some people may be more vulnerable to contaminants in drinking water than the general population. Immuno-compromised persons such as persons with cancer undergoing chemotherapy, persons who have undergone organ transplants, people with HIV/AIDS or other immune system disorders, some elderly, and infants can be particularly at risk from infections. These people should seek advice about drinking water from their health care providers.”
Want to ensure you have the cleanest, safest water in your home? Check out our water filter products HERE.


